Autoimmune diseases (ADs) represent a significant challenge in healthcare, affecting millions worldwide. These conditions arise when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. While current treatments for ADs focus on immunosuppression, they often come with significant side effects and provide only symptomatic relief. In recent years, there has been growing interest in cell-based therapies, particularly CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) cell therapy, as a potential solution to address the underlying causes of ADs.
Autoimmune diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease, among others. Despite their diverse manifestations, these diseases share a common underlying pathology of immune dysregulation. In healthy individuals, the immune system is finely tuned to distinguish between self and non-self antigens, but in autoimmune disorders, this distinction becomes blurred, leading to an attack on the body's own tissues.
CAR cell therapy offers a promising approach to treating ADs by depleting disease-driving immune cells and rebalancing immune homeostasis. CAR T cells, which are engineered to express synthetic receptors targeting antigens expressed on the surface of pathogenic cells, have shown remarkable success in treating certain cancers. Now, researchers are exploring the potential of CAR T cells and their counterparts, CAR iNK (natural killer) cells, in targeting the aberrant autoreactive cells implicated in autoimmune diseases to reset the immune sytsem1. We believe that cell therapy approaches could provide long-lasting drug-free remission and potentially a curative treatment for AD patients.
Understanding CAR Therapeutics
CAR T cell therapy first emerged as a groundbreaking treatment modality for hematological malignancies, such as leukemia and lymphoma. Building on this clinical success, researchers have recently turned their attention to applying CAR cell therapy to treat autoimmune diseases.
In the context of ADs, CAR T cells have been investigated for their ability to target autoreactive T cells or B cells. B cells, in particular, play a central role in many autoimmune disorders by producing autoantibodies and driving inflammation. One promising target for CAR cell therapy in ADs is the cell surface protein CD19. High-level expression of CD19 is maintained throughout the majority of B-cell differentiation stages. By targeting CD19-positive B cells, CAR T cells or CAR NK cells can selectively eliminate the autoreactive B cell populations responsible for driving autoimmune responses2.
A recent early clinical study showed promising results for using CD19 CAR T cell therapy to treat ADs. Patients with systemic sclerosis, severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and idiopathic inflammatory myositis showed remission following therapy3. However, CAR NK cell therapy may be beneficial over CAR T cell therapy, particularly in ADs that have dysfunctional T cells. CAR T cell therapy may also result in side-effects such as GvHD (Graft-versus-host disease, worsening the AD symptoms), neurotoxicity, and cytokine release syndrome; CAR NK cell therapy may offer a safer alternative4.
Despite the potential of CAR cell therapy in ADs, several challenges remain, including scalability, persistence, and off-target effects. Evotec's innovative approach to addressing these challenges involves the use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to generate allogeneic off-the-shelf CAR iNK cells with enhanced scalability and precision. iPSCs, reprogrammed from adult somatic cells, offer a potentially inexhaustible source of immune cells that can be genetically engineered and differentiated into various cell types to tackle a range of diseases.
iPSC-Derived CD19 CAR iNK Cells for Targeted B Cell Depletion
A study by researchers at Evotec investigated the performance of iPSC-derived CD19 CAR iNK cells as a novel therapeutic approach for ADs. Using Evotec’s validated GMP iPSC line, researchers produced genetically modified cells with a knock-in of CD19-CAR. The modified cells successfully differentiated into CD19 CAR iNK cells using a feeder-free 3D differentiation process, which could be confirmed by flow cytometry. The established protocol can ensure high purity and functionality of the resulting cells. Results showed that iNKs generated from the GMP iPSC line were homogenous and phenotypically comparable to blood-derived (BD) NK cells form healthy donors.
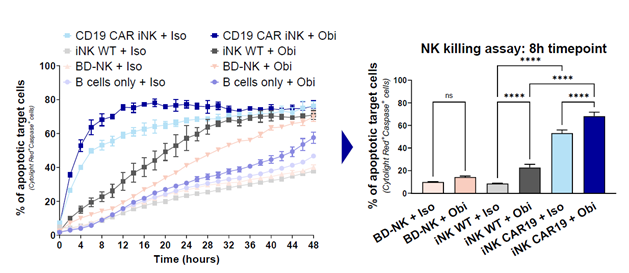
Figure 1: Cytotoxicity against SLE patient B cells. NK killing assays of effector cells - iNK without CAR (WT), CD19 CAR iNK or healthy donor BD NK cells (BD-NK) co-cultured 1:1 (E:T) with SLE patient B cells, + 10μg/ml anti-CD20 antibody (Obinutuzumab (Obi)) or isotype control (Iso) (n=2).
In vitro experiments demonstrated the cytotoxic effector function of CD19 CAR iNK cells in selectively targeting and eliminating CD19-positive B cells. Co-culture assays using patient-derived primary B cells from patients with SLE autoimmune disease, showed robust cytotoxicity of CD19 CAR iNK cells. The CD19 CAR iNK cells were more efficient than iNK cells without a CAR or BD NK cells in depleting the patient-derived primary B cells. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of CD19 CAR iNK cells in treating ADs, offering a targeted and scalable alternative to conventional immunosuppressive therapies.
Evotec's Scalable Therapeutics Approach
Evotec's commitment to allogeneic cell therapy innovation is exemplified by its scalable therapeutics approach, which leverages cutting-edge technologies and infrastructure to develop next-generation therapies for ADs. Central to this approach is the use of iPSCs as a platform for generating CAR iNK cells with enhanced scalability and precision. By introducing CARs targeting CD19 into iPSCs and differentiating them into iNK cells, Evotec aims to create scalable and precise off-the-shelf therapies for ADs.
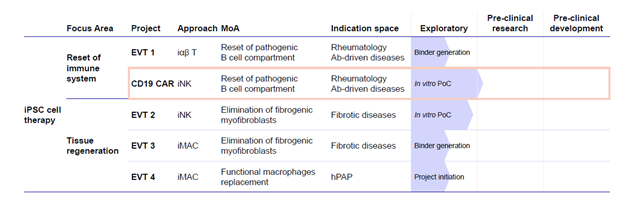
Figure 2: Evotec’s pipeline to co-create iPSC-based cell therapeutics with partners in Inflammation & Immunology.
Evotec's end-to-end process for iPSC-based therapeutics encompasses differentiation, gene editing, preclinical and clinical development, ensuring the efficient generation and characterization of CAR iPSC-derived cells. By utilizing validated GMP iPSC lines and GMP-compatible differentiation protocols, Evotec ensures the safety and quality of its allogeneic cell therapy products, paving the way for clinical translation.
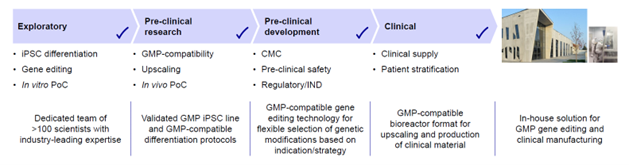
Figure 3: Evotec’s end-to-end process for iPSC-based therapeutics.
The scalability of Evotec's approach enables the production of large quantities of CAR iNK cells, making them suitable for widespread use in treating ADs. Additionally, the precision of iPSC-derived CAR iNK cells allows for targeted and personalized therapies tailored to individual patients' needs, reducing the risk of off-target effects and enhancing treatment efficacy.
Future Potential with Evotec
Evotec's iPSC-derived CD19 CAR iNK cells represent a promising new approach to treating autoimmune diseases. By harnessing the power of iPSC and CAR technology, allogeneic cell therapy can help revolutionize the treatment landscape for ADs, offering patients a targeted, scalable and potentially curative alternative to conventional therapies.
As research in this field continues to advance, Evotec remains at the forefront of allogeneic cell therapy innovation, driving the development of next-generation treatments for ADs (Figure 2). Evotec’s GMP-compliant production pipelines provides an efficient, reproducible, and scalable way to produce CAR iNK cells derived from iPSC for clinical development. With its commitment to precision medicine and scalable therapeutics, Evotec is well-positioned to meet the growing demand for effective and accessible off-the-shelf therapies for autoimmune diseases.
See more iPSC-based Cell Therapies for I&I Diseases
To discover more about this research, download our scientific poster
References:
(1) Blache, U.; Tretbar, S.; Koehl, U.; Mougiakakos, D.; Fricke, S. CAR T Cells for Treating Autoimmune Diseases. RMD Open 2023, 9 (4), e002907. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002907.
(2) Jin, X.; Xu, Q.; Pu, C.; Zhu, K.; Lu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Han, Y.; Lu, L. Therapeutic Efficacy of Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cells in a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18 (8), 1896–1903. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0472-1.
(3) Müller Fabian; Taubmann Jule; Bucci Laura; Wilhelm Artur; Bergmann Christina; Völkl Simon; Aigner Michael; Rothe Tobias; Minopoulou Ioanna; Tur Carlo; Knitza Johannes; Kharboutli Soraya; Kretschmann Sascha; Vasova Ingrid; Spoerl Silvia; Reimann Hannah; Munoz Luis; Gerlach Roman G.; Schäfer Simon; Grieshaber-Bouyer Ricardo; Korganow Anne-Sophie; Farge-Bancel Dominique; Mougiakakos Dimitrios; Bozec Aline; Winkler Thomas; Krönke Gerhard; Mackensen Andreas; Schett Georg. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Disease — A Case Series with Follow-Up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390 (8), 687–700. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2308917.
(4) Műzes, G.; Sipos, F. CAR-Based Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases: A Novel Powerful Option. Cells 2023, 12 (11), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12111534.
